Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9
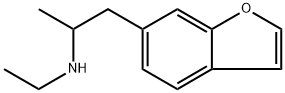
6-EAPB, also known as 1-(benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine, is a potentially psychedelic and potentially entactogenic drug of the benzofuran class;[1] it is structurally related to 6-APB and MDMA.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
6-EAPB is a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor.[2] It shows very low potency as a serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonist.[2]
Society and culture
Legal status
As an N-ethyl derivative of 6-APB, 6-EAPB fell outside the scope of the Temporary Class Drug ban issued by the Home Office on June 10, 2013.[3] The ACMD has advised that 6-EAPB (and other benzofurans) are moved to Class B,[4] this came into action on 10 June 2014. Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9
Structure
3D Structure
Properties
IUPAC Name |
1-(1-benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine | |
|---|---|---|
InChI |
InChI=1S/C13H17NO/c1-3-14-10(2)8-11-4-5-12-6-7-15-13(12)9-11/h4-7,9-10,14H,3,8H2,1-2H3 | |
InChI Key |
MIRNYUKRRZFBOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCNC(C)CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)C=CO2 | |
Molecular Formula |
C13H17NO | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9, Buy 6-EAPB Cas 1632539-47-9 | |
Molecular Weight |
203.28 g/mol | |
CAS No. |
1632539-47-9 |
Advanced Pharmacological Mechanisms of Action of 6 Eapb in Preclinical Models
In Vitro and Ex Vivo Neurotransmitter Transporter Interaction Studies
Studies employing in vitro and ex vivo methods, such as assays using human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells transfected with human transporters and experiments with rat brain synaptosomes, have been instrumental in characterizing the interaction of benzofurans with monoamine transporters. These studies assess compounds’ affinity for transporters, their ability to inhibit neurotransmitter uptake, and their capacity to induce neurotransmitter release.
Characterization of Dopamine (B1211576) Transporter (DAT) Affinity and Releasing/Uptake Inhibitory Potency
Research indicates that 6-EAPB exhibits affinity for the human dopamine transporter (hDAT). In one study, this compound demonstrated a rank order of affinity where hDAT affinity was greater than that for the norepinephrine (B1679862) transporter (hNET) and the serotonin (B10506) transporter (hSERT). Furthermore, this compound showed similar potencies for inhibiting the uptake of neurotransmitters at hDAT, hNET, and hSERT.
While specific data on this compound’s releasing potency at DAT from the search results is limited, studies on the structurally similar compound 6-APB provide relevant context. 6-APB has been characterized as a potent substrate-type releaser at DAT in rat brain synaptosomes and in HEK-293 cells transfected with human transporters. This activity suggests that, by structural analogy, this compound may also function as a substrate-type releaser at DAT, promoting the efflux of dopamine from presynaptic terminals.
Characterization of Norepinephrine Transporter (NET) Affinity and Releasing/Uptake Inhibitory Potency
Regarding the norepinephrine transporter, this compound has shown affinity for hNET, with its affinity being lower than that for hDAT but higher than for hSERT in one comparative analysis. Consistent with its effects at DAT and SERT, this compound displayed similar potencies in inhibiting the uptake of norepinephrine via hNET.
Similar to its effects at DAT, the related compound 6-APB acts as a potent substrate-type releaser at NET in rat brain synaptosomes and human transfected cells. This observation in 6-APB suggests that this compound may also possess the ability to induce norepinephrine release via interaction with NET.
Characterization of Serotonin Transporter (SERT) Affinity and Releasing/Uptake Inhibitory Potency
This compound’s interaction with the serotonin transporter has also been investigated. Studies have shown that this compound has affinity for hSERT, with its affinity being the lowest among the three monoamine transporters (hDAT > hNET > hSERT). Despite differences in affinity, this compound demonstrated similar potencies in inhibiting serotonin uptake via hSERT.
Data from 6-APB indicates it is a potent substrate-type releaser at SERT in both rat brain synaptosomes and human transfected cells. Notably, 6-APB was reported to be a fully efficacious releaser at hSERT in transfected cell assays. Based on structural similarities, this compound is likely to share this property of inducing serotonin release through SERT.
Comparative Analysis of Monoamine Releasing Properties in Synaptosomal Preparations
While direct, detailed data specifically on this compound’s monoamine releasing properties in synaptosomal preparations were not prominently featured in the search results, extensive research has been conducted on related benzofurans, particularly 6-APB. Studies using rat brain synaptosomes have demonstrated that 6-APB is a potent substrate-type releaser at DAT, NET, and SERT with nanomolar potencies. These benzofuran (B130515) compounds were found to be at least threefold more potent than MDA and MDMA at evoking transporter-mediated release in rat brain synaptosomes.
Given the structural similarities between this compound and 6-APB, and the observed uptake inhibition profile of this compound , it is highly probable that this compound also acts as a substrate-type releaser in synaptosomal preparations, promoting the release of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. The relative potencies and efficacy of this compound in inducing the release of each monoamine would require specific experimental validation, but the available data on related compounds strongly suggest a similar mechanism of action involving transporter-mediated release.
Receptor Binding and Functional Agonism Investigations
Beyond their interactions with monoamine transporters, benzofuran compounds have been investigated for their activity at various neurotransmitter receptors, particularly serotonin receptors.
Serotonin (5-HT) Receptor Subtype Interactions (e.g., 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B)
Specific binding and functional data for this compound at serotonin receptor subtypes were not extensively detailed in the search results. However, studies on the closely related compound 6-APB provide significant insights into the likely receptor profile of this compound.
6-APB has been shown to be a potent high-efficacy partial agonist or full agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor. Quantitative data for 6-APB at the 5-HT2B receptor includes a Ki of 3.7 nM, an EC50 of 140 nM, and an Emax of 70%. 6-APB is also a partial agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, with an EC50 of 5,900 nM and an Emax of 43%. Additionally, 6-APB shows affinity for the 5-HT2C receptor (Ki = 270 nM) and the 5-HT1A receptor (Ki = 1,500 nM).
Initial studies on both 5-APB and 6-APB consistently reported that they act as agonists at the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors. Most benzofurans, including 6-APB, have been characterized as partial 5-HT2A agonists and agonists at the 5-HT2B receptor. The 5-HT2A receptor is known to be coupled to the Gq/G11 signaling pathway. The 5-HT2B receptor is expressed in both the brain and peripheral tissues.
Based on the strong structural similarity between this compound and 6-APB, and the consistent findings regarding the agonistic activity of 6-APB and other related benzofurans at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, it is highly probable that this compound also interacts with these receptor subtypes as an agonist. Specific binding affinities and functional potencies for this compound at these receptors would require dedicated experimental determination.
Adrenergic Receptor (e.g., α2C) Affinities and Functional Activity
Adrenergic receptors, particularly the alpha-2 subtypes (α2A, α2B, and α2C), play a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitter release and cardiovascular function. While comprehensive data specifically on this compound’s affinity and functional activity at adrenergic receptors, including α2C, are limited in the provided search results, related benzofuran compounds have shown interactions with these receptors. For instance, 6-APB has been reported to bind with high affinity to the α2C-adrenergic receptor (Ki = 45 nM). Additionally, studies on 5-APB and 6-APB have indicated appreciable affinity toward α1A and α2A adrenergic receptors. The α2C receptor is known to modulate neurotransmission, particularly at lower levels of nerve activity. Further research is needed to specifically characterize this compound’s precise binding affinities and functional consequences at various adrenergic receptor subtypes.
Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 (TAAR1) Interactions
Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a G protein-coupled receptor expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in monoaminergic neurons, where it modulates the activity of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin systems. TAAR1 is activated by trace amines and also by various amphetamine analogs and structurally related drugs. Studies on related benzofurans, including 5-APB and 6-APB, have reported agonist or partial agonist properties at TAAR1 in rat, mouse, and human models. These interactions can lead to increased intracellular cAMP and influence neurotransmitter release. While direct data on this compound’s interaction with TAAR1 is not explicitly detailed in the provided snippets, the structural similarity to 5-APB and 6-APB suggests a potential for TAAR1 interaction. Benzofurans, including 5-EAPB, are listed as hTAAR1 agonists with an MDMA-like pharmacodynamic profile.
Comparative Preclinical Pharmacology with Structural Analogues (e.g., 6-APB, 5-EAPB, 6-MAPB, MDMA, MDA)
Preclinical pharmacological studies compare the effects of this compound to its structural analogues, such as 6-APB, 5-EAPB, 6-MAPB, MDMA, and MDA, to understand its relative potency and mechanism of action.
Research indicates that benzofuran compounds, including 5-APB and 6-APB, act as potent substrate-type releasers at dopamine transporters (DAT), norepinephrine transporters (NET), and serotonin transporters (SERT). They inhibit neurotransmitter uptake at these transporters in a dose-dependent manner. Compared to MDA and MDMA, 5-APB and 6-APB have been found to be more potent at evoking transporter-mediated release. For example, 6-APB was reported to be 10-fold more potent than MDA at DAT-mediated release and 4.5 times more potent than MDA at SERT-mediated release in rat brain synaptosomes.
While 5-APB and 6-APB show relatively low DAT:SERT inhibition ratios, consistent with greater serotonergic versus dopaminergic activity similar to MDMA, some studies suggest they can be more selective for inhibiting DAT.
5-EAPB, a structural isomer of this compound, has also been evaluated. One study reported that 5-EAPB exhibited a reduction in the magnitude of norepinephrine and dopamine release while maintaining 5-HT releasing properties compared to 5-APB. 5-EAPB was also found to be more potent at the DAT compared with MDMA and MDA in one study.
6-MAPB and 5-MAPB, N-methylated analogues, are also potent substrate-type releasers at DAT, NET, and SERT, and have been shown to be more potent than MDMA at these transporters.
In addition to transporter interactions, comparative studies highlight differences in receptor affinities. While 5-APB and 6-APB are agonists at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, unlike MDMA which is not a 5-HT2B agonist, most benzofurans are partial 5-HT2A agonists similar to MDMA. 6-APB also shows affinity for the 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A receptors.
The preclinical data collectively suggest that this compound and its analogues share similarities with MDMA and MDA in their ability to interact with monoamine transporters, acting as releasers. However, there are notable differences in potency and receptor profiles, particularly concerning 5-HT2B and potentially adrenergic receptors and TAAR1.
Data Table: Comparative In Vitro Potencies (EC50 nM) for Monoamine Release in Rat Brain Synaptosomes
| Compound | DAT Release (EC50 nM) | NET Release (EC50 nM) | SERT Release (EC50 nM) |
| MDA | 106 | 178 | 161 |
| MDMA | 337 | 300 | 90 |
| 5-APB | 31 | 57 | 19 |
| 6-APB | 10 | 66 | 36 |
| 5-MAPB | 34 | 80 | 36 |
| 6-MAPB | 19 | 48 | 36 |
6-(2-Aminopropyl)benzofuran hydrochloride, commonly referred to as 6-EAPB, is a synthetic compound that belongs to the class of aminoalkylbenzofurans. This compound is structurally related to other psychoactive substances and has garnered attention for its stimulant and entactogenic properties. It is often studied in the context of its potential effects on neurotransmitter systems, particularly its interaction with monoamine transporters.
6-EAPB is classified under the broader category of new psychoactive substances (NPS). It is chemically similar to other compounds such as 5-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran (5-APB) and has been associated with various recreational uses. The compound’s chemical identifier is 1823318-37-1, and it is available for research purposes from various chemical suppliers .
Methods
The synthesis of 6-EAPB hydrochloride typically involves a multi-step reaction process. The primary synthetic route includes the reaction of 6-bromo-1-benzofuran with N-ethyl-2-bromo-1-propanamine. This reaction is carried out under specific conditions using a solvent such as dimethylformamide (DMF) and a base like potassium carbonate (K2CO3) to facilitate the nucleophilic substitution reaction. After the initial reaction, the product is purified and converted into its hydrochloride salt form for stability and ease of handling .
Technical Details
The synthesis can be broken down into several key steps:
- Nucleophilic Substitution: The bromine atom in 6-bromo-1-benzofuran is replaced by the N-ethyl-2-bromo-1-propanamine.
- Solvent and Base Utilization: Dimethylformamide acts as a solvent, while potassium carbonate serves as a base to promote the reaction.
- Purification: The crude product undergoes purification processes such as recrystallization or chromatography to isolate the desired hydrochloride salt form .
Reactions
6-EAPB can undergo various chemical reactions:
- Oxidation: This can be achieved using agents like potassium permanganate or chromium trioxide, leading to the formation of carboxylic acids or ketones.
- Reduction: Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride or sodium borohydride can convert ketones or aldehydes into alcohols or amines.
- Substitution Reactions: Nucleophilic substitution can occur with reagents like sodium methoxide, leading to various substituted benzofuran derivatives .
Technical Details
Each type of reaction requires specific conditions:
The mechanism of action for 6-EAPB primarily involves its interaction with monoamine transporters, particularly the serotonin transporter (SERT) and dopamine transporter (DAT). Research indicates that 6-EAPB acts as a substrate-type releaser at these transporters, facilitating the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine.
Process and Data
In studies comparing 6-EAPB to other psychoactive substances, it was found that 6-EAPB has a higher potency than traditional stimulants like methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). For instance, it has been shown that 6-EAPB can induce significant release at SERT with an effective concentration (EC50) value around 36 nM, indicating strong activity at low concentrations .
Physical Properties
6-EAPB hydrochloride typically appears as a white crystalline solid. Its melting point and solubility characteristics are important for determining its stability and usability in laboratory settings.
Chemical Properties
The chemical stability of 6-EAPB can be influenced by factors such as pH and temperature. It exhibits typical reactivity patterns associated with amines and aromatic compounds, making it amenable to various chemical transformations.
Relevant Data or Analyses
Studies have shown that the compound’s solubility in water is limited but can be enhanced in organic solvents. Its stability under different environmental conditions remains an area of active research, particularly concerning its degradation pathways in biological systems .
Scientific Uses
6-EAPB has several applications in scientific research:
- Analytical Chemistry: It serves as an analytical reference standard for mass spectrometry and chromatography.
- Neuroscience: Researchers study its effects on neurotransmitter systems to understand its potential therapeutic applications.
- Forensic Toxicology: It is used to identify and quantify new psychoactive substances in biological samples .
Historical Context of Benzofuran Derivatives in Psychoactive Research
Benzofuran derivatives emerged as significant subjects in psychoactive research following initial investigations into their structural and functional analogs of phenethylamines. The foundational compound 6-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran (6-APB), first synthesized in 1993 by David E. Nichols, was conceived as a non-neurotoxic alternative to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) due to its benzofuran core replacing the traditional methylenedioxyphenyl ring [1] [4]. Early pharmacological studies revealed that 6-APB acts as a potent serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA), with high selectivity for the 5-HT₂B receptor—a characteristic linked to both entactogenic effects and potential cardiotoxicity [1] [2]. By the 2010s, 6-APB and its isomers (e.g., 5-APB) entered recreational markets under branded names like “Benzofury,” capitalizing on their structural ambiguity to evade drug legislation [1] [4]. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) first detected 5-APB in 2010 and 6-APB in 2011, marking benzofurans as established novel psychoactive substances (NPS) within Europe’s rapidly diversifying drug landscape [2] [3].
Emergence of 6-EAPB as a Novel Psychoactive Substance (NPS)
6-EAPB (1-(benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine) represents a deliberate structural modification of 6-APB, where the primary amine is substituted with an N-ethyl group. This alteration was designed to circumvent regulatory controls targeting the parent compound [5]. Following the UK’s 2013 Temporary Class Drug Order banning 6-APB, 6-EAPB gained traction in online markets as a “legal high” due to its exclusion from analog-specific legislation [5]. Chemically classified as an N-alkylated benzofuran, 6-EAPB shares core features with entactogens like MDMA but exhibits distinct physicochemical properties, such as altered receptor-binding affinities and metabolic pathways [5] [10]. Its emergence exemplifies “law evasion” design principles pervasive in the NPS market: slight molecular tweaks preserve psychoactivity while avoiding legal restrictions [8] [10]. By 2014, the UK Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) recommended reclassifying 6-EAPB as a Class B drug, acknowledging its misuse potential [5]. Despite this, empirical data on 6-EAPB’s prevalence, pharmacology, and user demographics remain scarce compared to 6-APB, reflecting challenges in monitoring structurally fluid NPS families [3] [6].
Research Significance and Gaps in 6-EAPB Studies
The study of 6-EAPB is critical for understanding the neuropharmacological impact of N-alkyl modifications in benzofuran-based NPS. Preliminary evidence suggests that N-substitution alters monoamine transporter activity; for instance, N-methylated analogs like 5-MAPB exhibit enhanced dopamine release potency compared to non-alkylated counterparts [2]. However, 6-EAPB’s specific pharmacodynamic profile—including its affinity for serotonin (SERT), dopamine (DAT), and norepinephrine (NET) transporters—remains unquantified [2] [10]. Significant knowledge gaps persist in four areas:
- Mechanistic Studies: No in vitro or in vivo data elucidate 6-EAPB’s efficacy as a monoamine releaser or reuptake inhibitor.
- Metabolism: Phase I/II metabolic pathways are undefined, though rat studies of 6-APB suggest furan ring hydroxylation and cleavage as primary metabolic routes [1].
- Behavioral Effects: Unlike 6-APB, which induces locomotor activation in rats via monoamine release, 6-EAPB’s psychoactive properties are inferred solely from user anecdotes [2] [4].
- Analytical Detection: Standardized assays for identifying 6-EAPB in biological matrices are underdeveloped, hampering clinical and forensic case reporting [6] [8].Addressing these gaps is essential for evidence-based policymaking and public health responses to NPS threats [6] [8].
Table 1: Structural Evolution of Key Benzofuran-Derived NPS
| Compound | Chemical Name | Core Modification | Year First Detected | Legal Status (as of 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-APB | 6-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran | None (parent compound) | 2011 [2] | Class B (UK), Schedule III (CA) |
| 6-MAPB | 6-(2-methylaminopropyl)benzofuran | N-methylation | 2013 [2] | Class B (UK) |
| 6-EAPB | 1-(benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine | N-ethylation | ~2014 [5] | Class B (UK since 2014) |
| 5-APB | 5-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran | Benzofuran ring isomerization | 2010 [2] | Class B (UK) |
Table 2: Critical Research Gaps for 6-EAPB
| Domain | Specific Gap | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacology | Affinity for DAT/SERT/NET (Ki values) | High |
| Neurochemistry | In vivo monoamine release potency (EC₅₀) | High |
| Metabolism | Phase I/II metabolic pathways | Medium |
| Detection | Analytical standards for toxicological screening | High |
| Epidemiology | Prevalence in drug seizures or user populations | Low |
Properties
CAS Number
Product Name
IUPAC Name
Molecular Formula
Molecular Weight
InChI
SMILES
Synonyms
Product FAQ
Top Search Product Suppliers
Metabolic Pathways and Biotransformation of 6 Eapb in Animal and in Vitro Systems
See also
References
- Taschwer M, Hofer MG, Schmid MG (October 2014). “Enantioseparation of benzofurys and other novel psychoactive compounds by CE and sulfobutylether β-cyclodextrin as chiral selector added to the BGE”. Electrophoresis. 35 (19): 2793–2799. doi:10.1002/elps.201400164. PMID 24930967. S2CID 2937770.
- Stalberga, D., Kronstrand, R., Schranz, B., van Zijl, N., Karlman, S., Aref, S., … & Gréen, H. (2025). Comprehensive in vitro profiling of traditional and emerging stimulants at monoamine transporters and the 5HT2A receptor. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.176253891.19158813/v1
- “Temporary class drug order on benzofury and NBOMe compounds”. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- “ACMD recommends permanent ban on two “legal highs””. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- “Ban on NBOMe and benzofurans comes into force”. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
-
Buy Online CAS Number 1632539-47-9 – TRC – 6-EAPB | LGC …
Purchase online CAS Number 1632539-47-9 – TRC – 6-EAPB. High Quality CRMs, Reference Materials, Proficiency Testing & More at LGC Standards.
-
6-EAPB | 1632539-47-9 – ChemicalBook
6-EAPB (1632539-47-9) information like chemical properties,Structure,melting point,boiling point,density,molecular formula,molecular weight, physical …
-
Buy 6-EAPB (EVT-1487055) | 1632539-47-9 – ev
6- (2-Aminopropyl)benzofuran hydrochloride, commonly referred to as 6-EAPB, is a synthetic compound that belongs to the class of aminoalkylbenzofurans. This compound is structurally related to other …
-
Buy 6-EAPB – Express Highs
To understand it, it is important to fully grasp its chemical origins and makeup. 6-EAPB belongs in a class of substances called benzofuran. This class is represented by a heterocyclic compound that is …
-
6-EAPB (1632539-47-9) for sale
VulcanChem offers qualified products for 6-EAPB (CAS No. 1632539-47-9), please inquire us for more detail.
-
6-EAPB TR-E294000 | CymitQuimica
Technical inquiry about: TR-E294000 6-EAPB If you want to request a quotation or place an order, please instead add the desired products to your cart and then request a quotation or order from the cart.
-
Buy 6- [2- (Ethylamino)propyl]benzofuran | 1632539-47-9 | BenchChem
Benchchem offers qualified products for CAS No. 1632539-47-9 (6- [2- (Ethylamino)propyl]benzofuran), please inquire us for more detail.
-
6-EAPB – Chemical Route
IUPAC-name 1- (benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine. Synonyms 6-EAPB, 6- (2-Ethylaminopropyl)Benzofuran. Formal name N-ethyl-α-methyl-6-benzofuranethanamine. Cas number …
-
6-EAPB – ChemBK
Name:6-EAPB,CAS:1632539-47-9.Molecular Fomula:C13H17NO,Molar Mass:203.29,MSDS,Hazard,Safety.
-
1632539-47-9 | | 6-EAPB | iChemBio
6-EAPB. CAS: 1632539-47-9. 货号: iCB0246940. MDL Number: . 分子式: C13H17NO. 分子量: 203.29. iChemBio.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.